In my last post I talked about how the Citrix Receiver authenticates to a StoreFront server. In this post, I want to talk about resource enumeration with Citrix Receiver <> StoreFront <> XenDesktop deployments.
Before I go into the technical aspects of the way Citrix enumerates published resources, I want to briefly explain the history behind the Citrix XML Broker, as well as how the Citrix client enumerates published resources. In case anyone is interested in a broader history of Citrix, I encourage you to check out the 20 years of Citrix History publication that was published in 2009.
Citrix NFuse and the XML Portal Server
Back in 2000, Citrix signed a licensing deal with Sequoia Software (whom they later acquired in 2001) to integrate the NFuse as the foundation for providing an extensible application portal for MetaFrame. The XML Portal Server (XPS) technology was then built around NFuse to provide the ability to dynamically enumerate and present resources to end users. This integration was critical in giving Citrix the ability to stand apart from the competition (terminal services), and was the reason the next version of MetaFrame had the XP designation:
Since it’s introduction back in 2000, the NFuse protocol has remained at the core of every Citrix desktop/application virtualization product by way of the ‘XML Broker’ service. This service was included in all future releases, including all versions of XenApp & XenDesktop. Until XenDesktop 5 was released, the XML broker service ran as it’s own standalone service. During the XenDesktop ‘Storm’ site architecture rework (now called FMA, aka NOT IMA) the XenDesktop product team decided to relocate the XML broker service to run as a ‘virtual’ service by piggy-backing on the XenDesktop Broker service. Other than this move to virtualize the XML broker service, the service remains as NFuse capable as the XML broker service used in MetaFrame.
Because of the NFuse protocol, resource enumeration has remained compatible as MetaFrame evolved into XenDesktop. In other words, the old MetaFrame Web Interface Server would still enumerate published desktops from a XenDesktop 7 DDC, and a StoreFront 2.0 server would enumerate published applications from a MetaFrame XP XML broker service (theoretically at least!), as long as the requests are NFuse compatible.
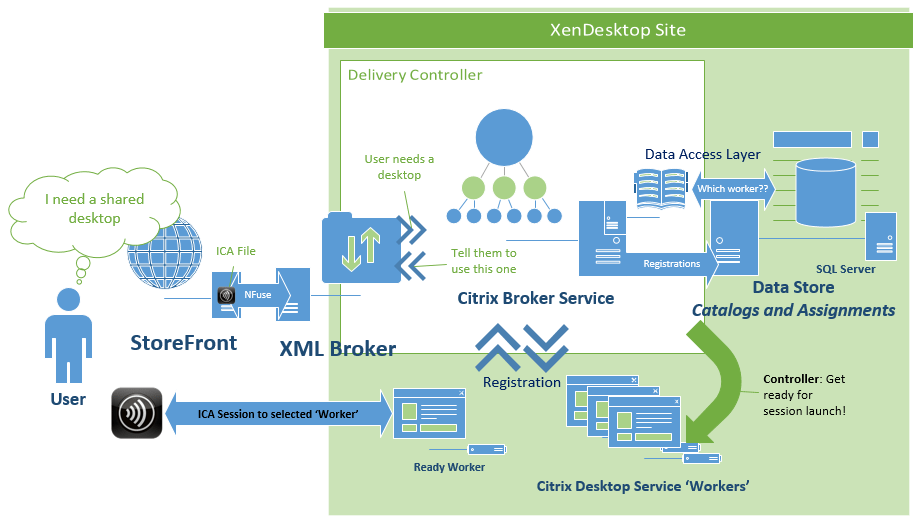
One of the main reasons the NFuse protocol is so durable is that it’s able to negotiate capabilities. In this example, a StoreFront site contacts a XenDesktop XML broker to determine what capabilities it has, and what resources are published to the authenticated user:
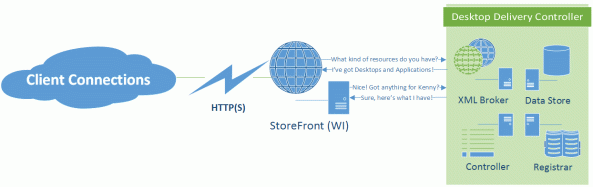
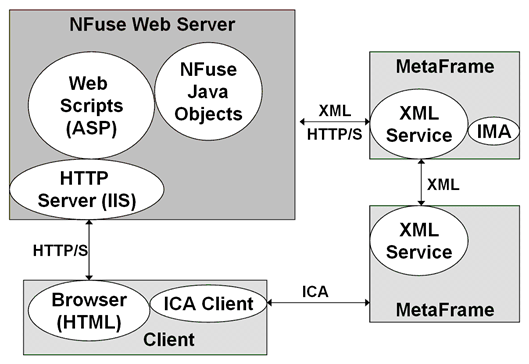
In this process, the web front-end server sends an XML message to the configured XML broker to request a list of capabilities. The XML broker then responds with an XML formatted list of the types of resources it has access to. StoreFront will then request any compatible resources for the the authenticated user account. The XML broker then works with the XenDesktop broker and controller services to find out what resources are assigned to the user. The enumerated resources are consumed by StoreFront and presented to the end user. This figure from the NFuse Classic 1.7 is still mostly relevant, just different companion components:
StoreFront & Receiver
With Citrix Web Interface, the results of application enumeration were presented all at once to the authenticated user (optionally sorted into tabs and/or folders). In other words, all resources published to a user would be shown to them, though you could hide resources as needed. StoreFront with Receiver added the functionality that was originally introduced with Citrix Merchandising Server and Dazzle, which is to allow a user to pick their ‘favorite’ resources, providing Self-Service ‘App Store’ functionality and allowing a user’s favorite resources to follow them across multiple client devices and device types.
Prior to Dazzle/Receiver, applications were either enumerated in a web browser using a Web Interface ‘Web’ site, or enumerated directly by the Citrix client agent through a ‘Services’ site. In the past three years the Citrix client has evolved from the ‘Online Plug-in’ to the Receiver for Windows.

The concept of client-side agent enumeration began with the ‘Program Neighborhood’ client (pre Online Plug-in), which would access a Services site (hence the default name PNAgent), and looked like this:
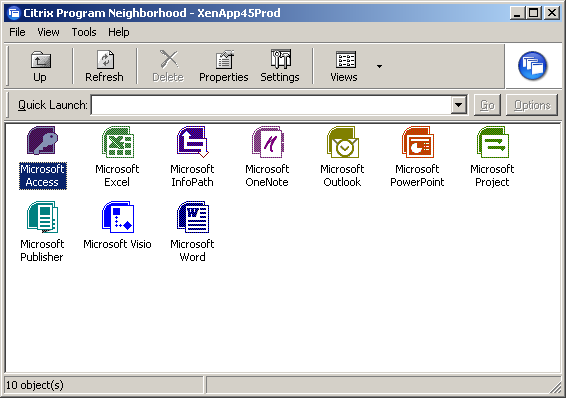
Until XenApp replaced Presentation Server, this was the way users would typically connect to applications, as the web portal wasn’t nearly as solid as the old WI server running in IE 5/6. By the time XenApp was released, Citrix decided to rework the ‘PNAgent’ to display resources as a system tray icon jump menu (which remains a fan favorite, quick, easy, intuitive) in what was first called the XenApp Plug-in, and later renamed to the Online Plug-in when XenDesktop was released:
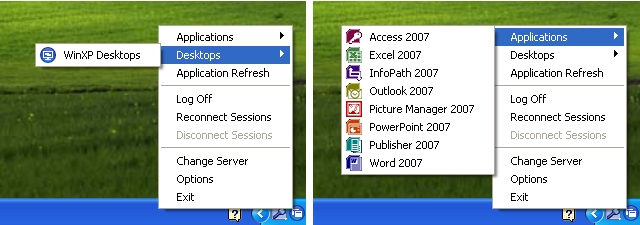
However, around the time the Apple App Store was released, and Windows Vista changed some application UI design consideration, Citrix decided to create a self-service framework by way of Dazzle and Merchandising Server. As a result of this they decided to do away with the notification icon ‘jump-menu’ since it didn’t align with Microsoft’s general UI design recommendations for Windows Vista/7. When Receiver was launched, this legacy ‘PNAgent’ functionality was taken out of the standard ‘Receiver’, and moved to only be included in the ‘Enterprise’ flavor of the Receiver, which is really just a nice way to say that they’re accommodating ‘Enterprise’ customers who still want/need to use this legacy functionality.
As of Receiver Enterprise (the black icon) PNAgent enumerated shortcuts are only available in the start-menu or desktop (according to the site/farm settings):
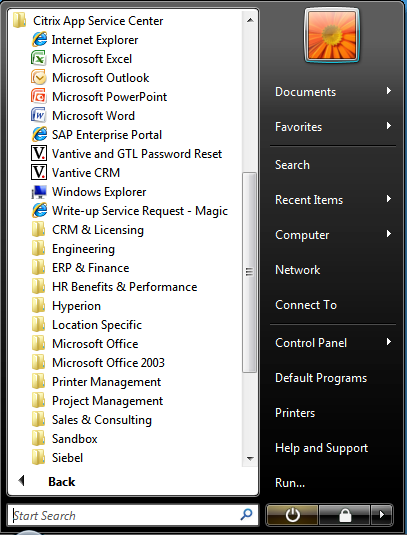
Citrix’s current preferred method of displaying shortcuts to end-users is using Receiver 3/4 to connect to a StoreFront Store, which uses the ‘Dazzle’ framework to present shortcuts:
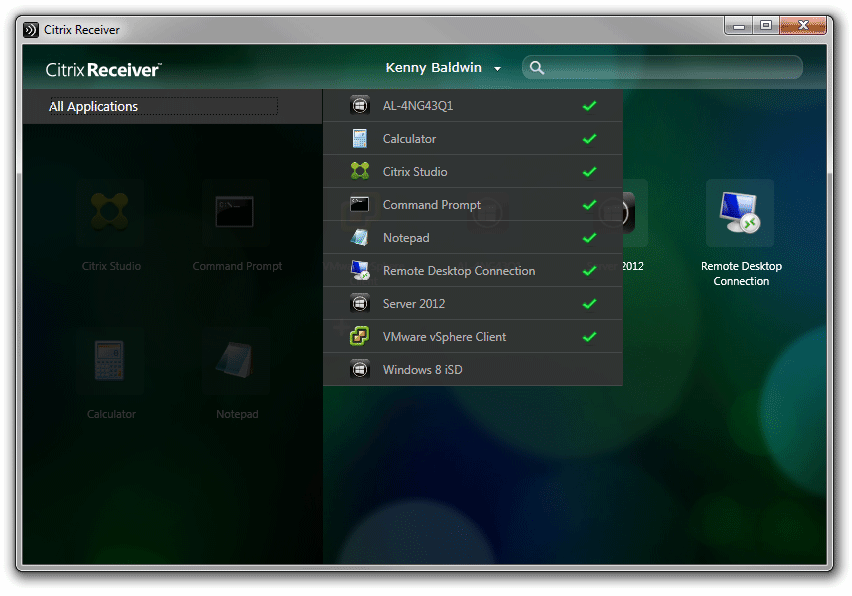
The StoreWeb StoreFront site aims to provide the same look and feel for users that aren’t enumerating via the ‘Receiver’ agent:
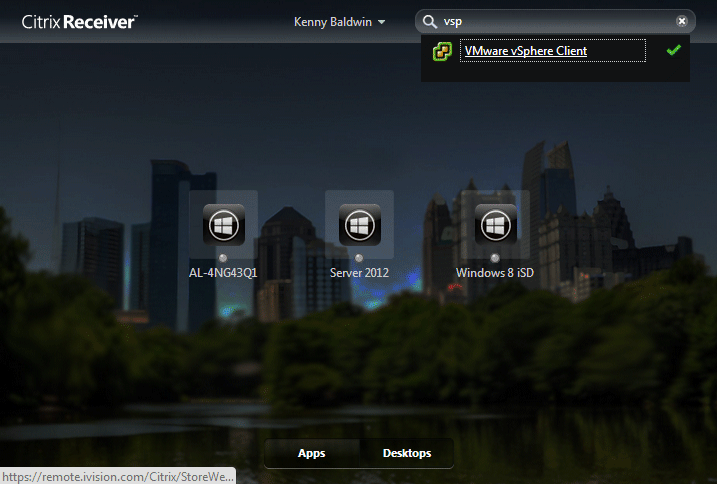
Connecting from mobile receivers maintains this consistency of favorite resources:
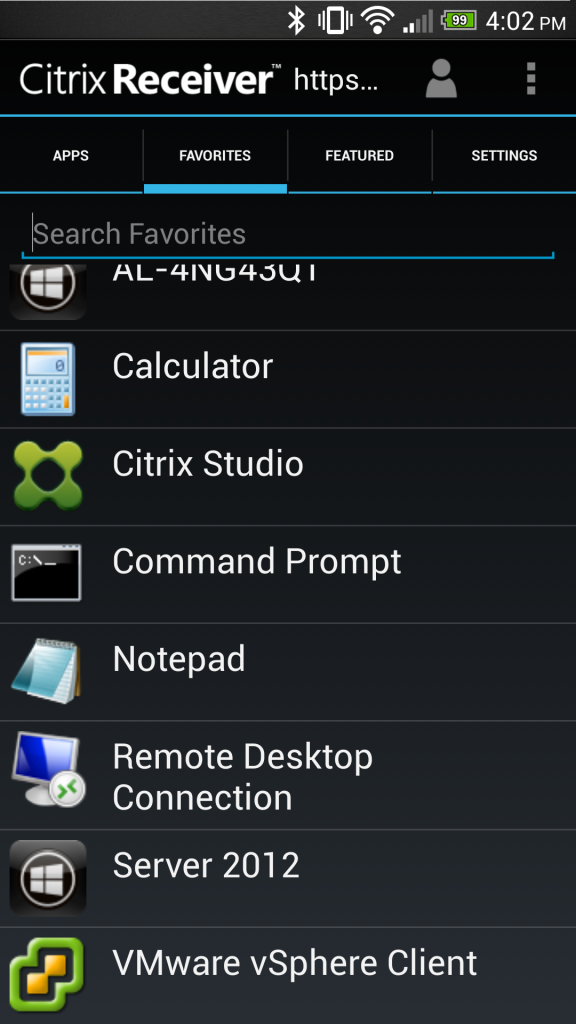
I could go on and on about the technical details of enumeration, but am out of time for today. I encourage readers to check out my previous post on the XML broker for a technical example of NFuse transactions.
In my next post I go into more detail about how enumerated resources are brokered to the receiver.